
Challenge 6 - Dapr MQTT Input Binding
< Previous Challenge - Home - Next Challenge >
Introduction
In this challenge, you’re going to add a Dapr input binding in the TrafficControlService. It’ll receive entry- and exit-cam messages over the MQTT protocol.
Description
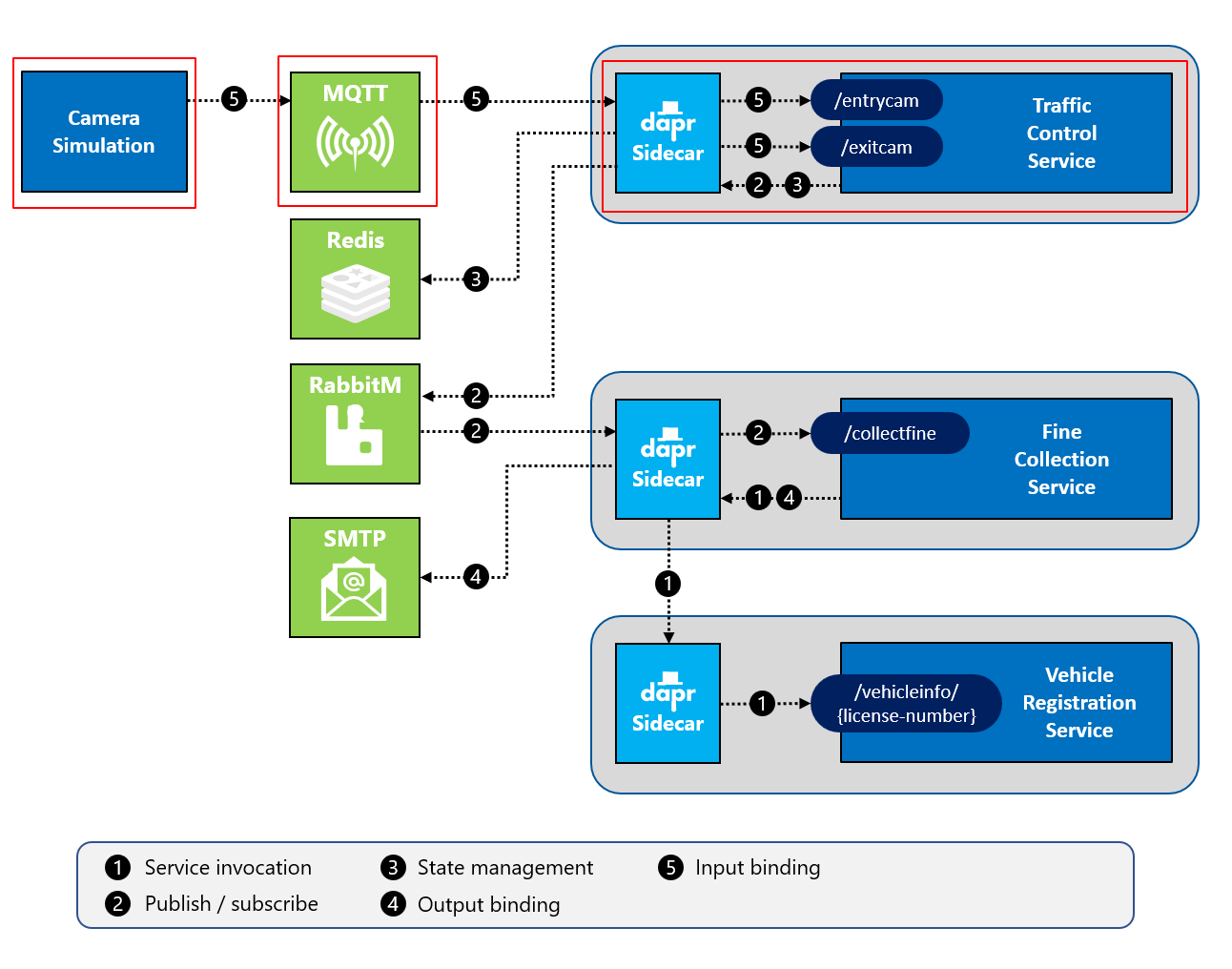
In this challenge you’ll focus on Dapr input bindings. The following diagram depicts how input bindings work:

For this hands-on challenge, you will add an input binding leveraging the Dapr binding building block. In the previous challenge, you implemented a Dapr output binding.
- Stand up a Mosquitto MQTT message broker in a Docker container.
- Modify the
TrafficControlService(TrafficControllerclass) to use the Dapr MQTT input binding to receive entry-cam and exit-cam messages over the MQTT protocol. - Modify the
Simulationapp to puttrafficcontrol/entrycam&trafficcontrol/exitcammessages on the MQTT queue.- Create a new class called
MqttTrafficControlServiceto do this (look at theHttpTrafficControlServiceas an example). - Modify the
Programclass to use this new service.
- Create a new class called
- Create a Dapr configuration file for specifying the Dapr SMTP input binding components.
- Restart all services & run the Simulation application.
- Once you have the solution running locally, modify the code to use Azure IoTHub & EventHub as the MQTT message broker.
Success Criteria
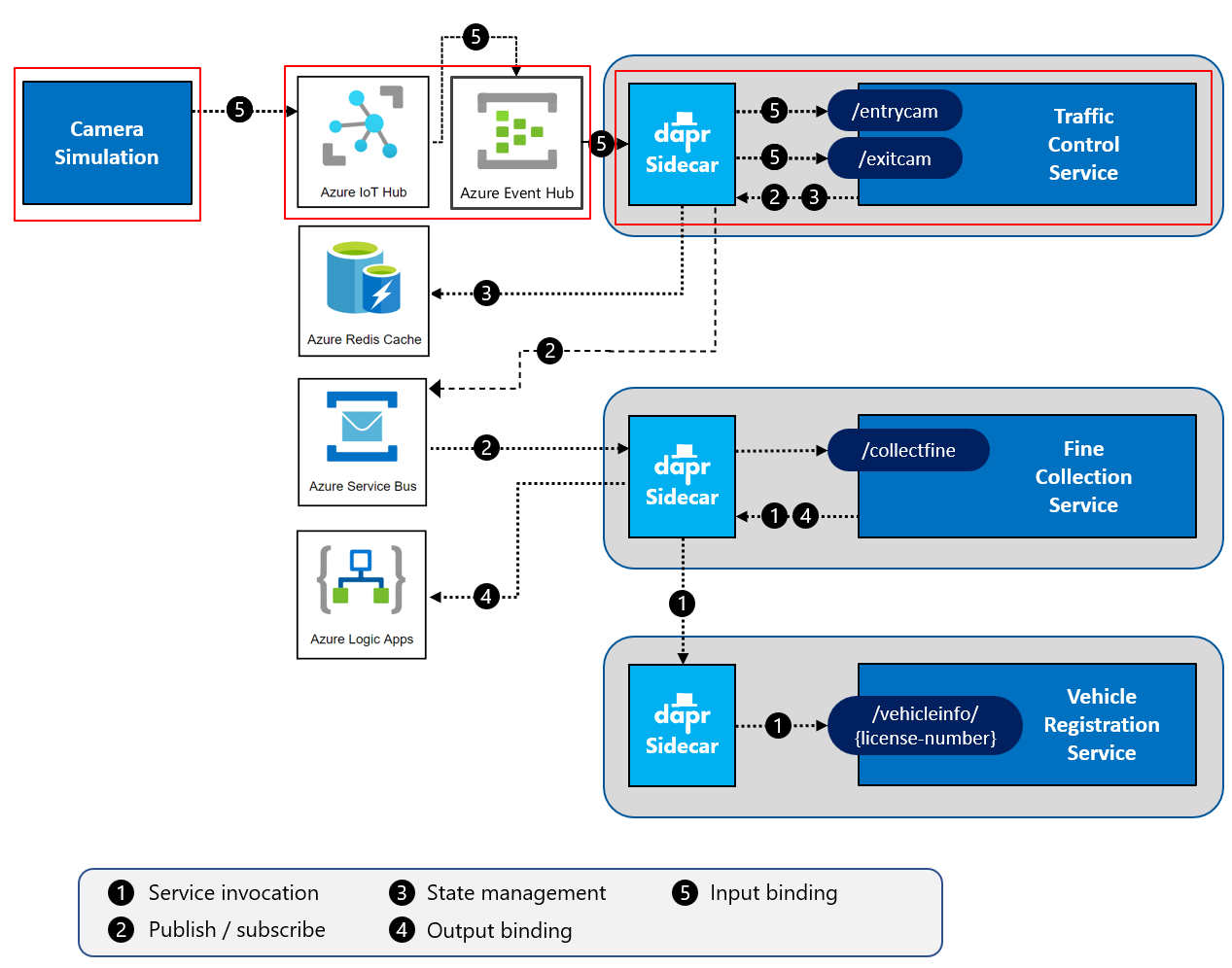
This challenge targets the operation labeled as number 5 in the end-state setup:
Local
Azure
- Validate that the Mosquitto MQTT message broker service is running locally.
- Validate that the
TrafficControlServicereceives messages via its Dapr component. - Validate that the Simulation application publishes entry-cam and exit-cam messages to the MQTT broker.
- Validate that messages are being sent through the Azure IoT Hub & EventHub.
DIY instructions
- Use MQTT broker Mosquitto for local development.
-
In order to connect to Mosquitto, you need to pass in a custom configuration file when starting it. With Docker, you can pass a configuration file when starting a container using a Volume mount. The folder
Resources/Infrastructure/mosquittoalready contains a config file you can use.-
Open a terminal window in VS Code and make sure the current folder is
Resources/Infrastructure/mosquitto. -
Start a Mosquitto MQTT container by entering the following command: When running on Windows:
docker run -d -p 1883:1883 -p 9001:9001 -v $pwd/:/mosquitto/config/ --name dtc-mosquitto eclipse-mosquittoWhen running on Mac or Linux:
docker run -d -p 1883:1883 -p 9001:9001 -v $(pwd)/:/mosquitto/config/ --name dtc-mosquitto eclipse-mosquitto
This will pull the docker image
eclipse-mosquittofrom Docker Hub and start it. The name of the container will bedtc-mosquitto. The server will be listening for connections on port1883for MQTT traffic.The
-vflag specifies a Docker volume mount. It mounts the current folder (containing the config file) as the/mosquitto/config/folder in the container. Mosquitto reads its config file from that folder. -
-
To peak into the Mosquitto server, open a new terminal window and execute the following command:
docker logs dtc-mosquitto - Add the following MQTT configuration flags when connecting to the Mosquitto MQTT queue.
var configuration = new MqttConfiguration() { KeepAliveSecs = 60, Port = 1883 }; -
Use Azure IoT Hub & EventHub for deployments to Azure.
-
Create a IoT Device in Azure IoT Hub to represent your Simulation app.
az iot hub device-identity create --device-id simulation --hub-name <iot-hub-name> -
Get the IoT Hub Connection String for the device you just created.
az iot hub device-identity connection-string show --device-id simulation --hub-name <iot-hub-name> -
Use the
Microsoft.Azure.Devices.ClientNuGet package to connect to the IoT Hub instead of the local MQTT broker.
-